No documentation found for this version. Showing the latest available.
3.1. Database
This object is the basis of modeling and represents the database to be created in a PostgreSQL server as well as the model itself. All objects manipulated in pgModeler are directly or indirectly linked to it, meaning that some operations applied to the database object can affect some of its children. Database objects are unique instances and can't be copied from one model to another. The first tab of the database's dialog contains the following attributes:
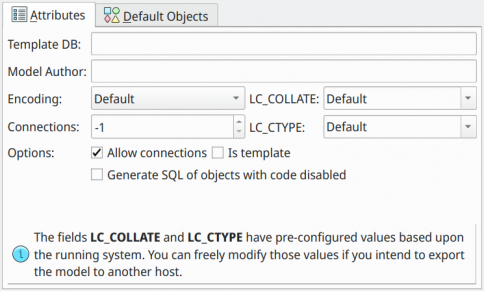
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
Template DB |
The name of the template database from which to create the new database. If this field is left empty, then the default template template1 is used. |
Model Author |
Name of the person who designed the model. The value specified here will be shown as a comment entry in the SQL definition of the model. |
Encoding |
The charset to be used in the database. If the Default value is used, then the charset will be configured by PostgreSQL depending on its settings. |
Connections |
The number of simultaneous connections that the database accepts. The default value -1 indicates that there is no limit for concurrent connections. |
LC_COLLATE |
Specifies in which language the string sorting must be applied. The values listed in this field are platform-dependent, so if you don't know what value to use, it's safe to leave it as Default. You can even specify a value not listed in this field; just type the desired value, then it'll override any value configured previously. |
LC_CTYPE |
Specifies in which language the character categorization (upper, lower, and digit) must be applied. The values listed in this field are platform-dependent, so if you don't know what value to use, it's safe to leave it as Default. You can even specify a value not listed in this field, just type the desired value then it'll override any value configured previously. |
Allow connections |
Indicates whether the database should allow clients to connect to it. |
Is template |
Indicates whether the database is a template one. |
Generate SQL of object with code disabled |
Indicates whether the SQL definition of objects with code disabled must appear in the whole database definition script. This option, when checked, is useful to diminish the size of the SQL script that defines the whole database since it'll exclude commented SQL code that defines disabled objects. |
There is another tab in the database editing form where default objects can be configured. Default objects are the ones that will be assigned to objects each time a new one is constructed. The default objects can be collation, schema, owner, and tablespace.
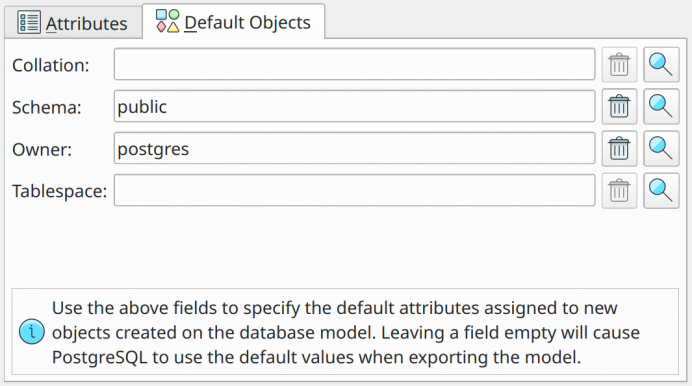
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
Collation |
Default collation assigned to any object created in the database model that makes use of this kind of object. |
Schema |
Default schema assigned to any object created in the database model that makes use of this kind of object. |
Owner |
Default owner assigned to any object created in the database model that makes use of this kind of object. |
Tablespace |
Default tablespace assigned to any object created in the database model that makes use of this kind of object. |
Apr 25, 2025 at 08:38