3.13. Collations
Collations are objects which allow specifying the sorting mode and character classification behavior either per column or per operation. Collations can be used to override the way data is sorted in a database even if this one has its modes defined by LC_COLLATE and LC_CTYPE attributes.
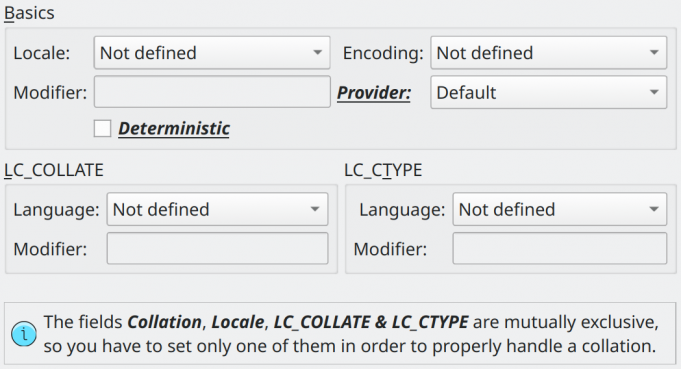
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
Collation |
This field can be used to create a new object from an existing collation. |
Locale |
This is a shortcut to specify the attributes LC_COLLATE and LC_CTYPE. |
Encoding |
Charset in which the collation works. |
Modifier |
Present in Basics, LC_COLLATE, and LC_LOCALE groups this field can be used to provide extra modifiers (like custom currency code) to a certain locale. |
Provider |
The provider attribute specifies the provider to use for locale services associated with a collation, like libc or icu. |
Deterministic |
Indicates that the collation is a deterministic one. A deterministic collation uses deterministic comparisons, which consider strings that are not byte-wise equal to be unequal even if they are considered logically equal by the comparison. |
LC_COLLATE |
This group of fields is used to determine in which language the string sorting must be applied. |
LC_CTYPE |
This group of fields is used to specify in which language the character categorization (upper, lower, and digit) must be applied. |
Note: the attributes Collation, Locale, LC_COLLATE, and LC_CTYPE are mutually exclusive, thus you can't use all of them at once.
Apr 3, 2023 at 16:35